A 3-D robust seismic ray
tracer
for volcanic regions
Seismic velocity structure of volcanic region is highly heterogeneous so that tools for investigation on the seismic properties of volcano should be robust for the velocity heterogeneity. A 3-D robust seismic ray tracer (Fermat), effective in any complicated velocity structure, is developed by using a hybrid scheme of the shortest path calculation and the downhill simplex optimization method. An accurate scheme of node configuration necessary for the 3-D shortest path calculation is employed in Fermat.

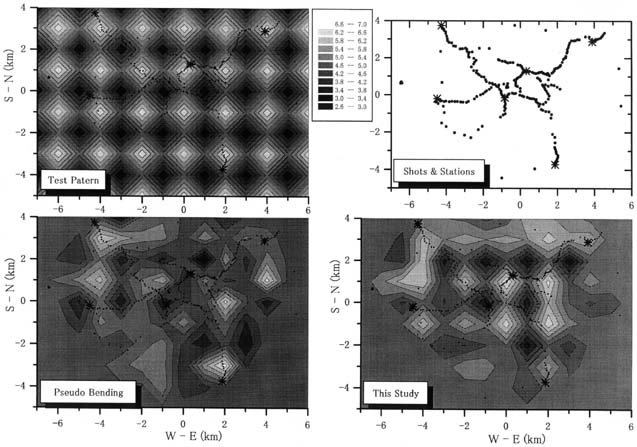
Fig.1: Results of the checkerboard test for travel time tomography using the shots and stations configuration (top right) of Project ASO98 (Seismic explosions) (Sudo, 1999). Solid dots and asterisks indicate the stations and shots respectively. Checkerboard pattern (top left) is for a depth of 1 km. A bottom left and bottom right are the results of velocity inversion with a pseudo bending ray tracer and Fermat, respectively.
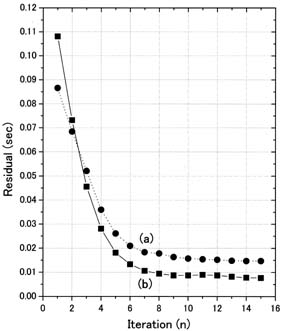
Fig.2: Travel time residuals of the theckerboard test shown in Fig.1. Comparison of inversion with (a) pseudo bending and (b) Fermat clearly shows that travel time residuals are halved by Fermat.
Nishi, K. (2001): A three dimensional robust seismic ray tracer for volcanic regions, Earth Planets Space, 53, 101-109.
The source code of Fermat (written in Fortran 90) is downloadable for the non-commertial use only.
If you would like to use the software, send an email to Kiyoshi NISHI ()
describing your Name/Institution/E-mail address/How do you use Fermat.Users will be registered for the future update and bug-fix.